A brute force attack is kind of a cyber attack where you try all the keys in key pool and eventually find the correct one. 5% of confirmed data breach incidents in 2017 were due to brute force attacks.
Brute gravity attacks are simple and reliable. Attackers let a computer do the work variegated combinations of usernames and passwords. Catching and neutralizing a brute gravity wade in progress is the weightier counter. Once attackers have wangle to the network, they’re much harder to catch.
Types of Brute Force Attacks
The most brute gravity wade is a wordlist attack, where the attacker works through a wordlist of possible passwords and tries them all. Wordlist attacks start with some assumptions well-nigh worldwide passwords to try to guess from the list in the dictionary. These attacks tend to be somewhat outdated, given newer and increasingly constructive techniques.
Recent computers manufactured within the last 10ish years can brute gravity one-liner an 8 weft alphanumeric password – capitals and lowercase letters, numbers, and special notation – in well-nigh two hours. Computers are so fast that they can brute gravity decrypt a weak encryption hash in mere months. These kinds of brute gravity attacks are known as an exhaustive key search, where the computer tries every possible combination of every possible weft to find the right combination.
Credential recycling is flipside type of brute gravity wade that reuses usernames and passwords from other data breaches to try to unravel into other systems.
The reverse brute-force wade uses a worldwide password like “password,” and subsequently tries to brute gravity a username to go with that password. Since “password” is one of the most worldwide passwords in 2017, this technique is increasingly successful than you might think.
Tips Behind Brute Force Attacks
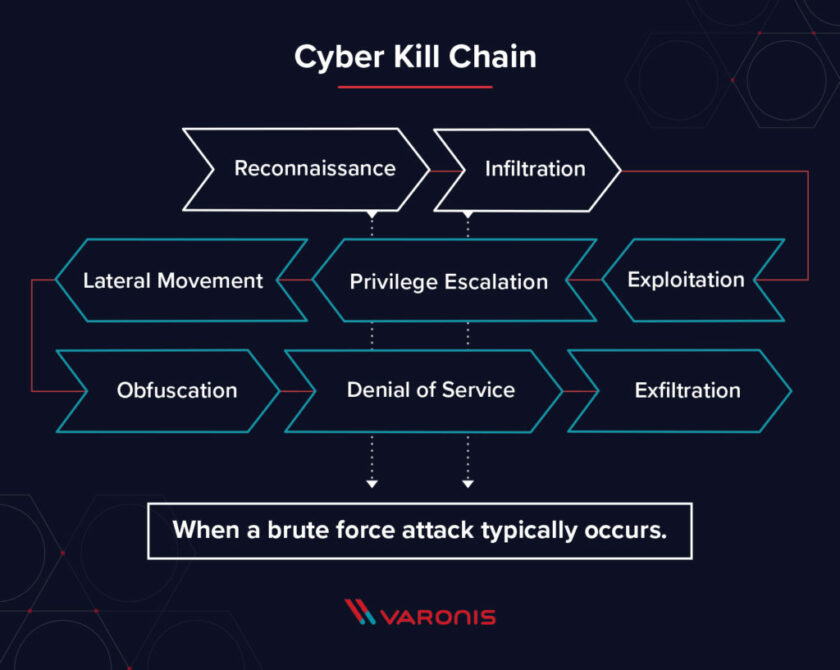
Brute gravity attacks occur in the early stages of the cyber skiver chain, typically during the infiltration stages. . Once they have entered into the network, hackers can use brute gravity techniques to climb their privileges or to run encryption downgrade attacks.
Attackers moreover use brute gravity attacks to squint for hidden web pages. Hidden web pages are websites that live on the internet, but are not linked to other pages. A brute gravity cross tests colourful addresses to see if they return a valid webpage, and will seek out a page they can exploit.
There is little finesse involved in a raw gravity attack, so attackers can automate multiple attacks to run in parallel to expand their options and find a positive outcome for themselves.
How to defend versus brute gravity attacks

Brute gravity attacks need time to run. Some attacks can take weeks or plane months to provide anything usable. Most of the defences attacks involve increasing the time required for success attitude ; technically possible, but that is not the only defence.
- Increase password length: Increasingly characters equal increasingly time to brute gravity crack
- Increase password complexity: More options for each weft moreover increase the time to brute gravity crack
- Limit login attempts – raw gravity attacks increment a counter of failed login chances on most directory services. A good defence against raw gravity attacks is to lock users out without a few failed tries.
- Implement Captcha: Captcha is a worldwide system for verifying that a human is a human on websites it can stop force gravity attacks in progress.
- Use Multi-Factor Identification – Multi-Factor Seal adds a second layer of security to every login issue that requires human intervention.
The energetic way to stop gravity attacks starts with monitoring. Varonis monitors Active Directory concerns and VPN traffic to detect raw severity attacks in progress. We have threat models that monitor blocking behaviours, threat models that identify potential credential stuffing, and increasingly all designed to detect and prevent brute gravity attacks that overcome crossing climbs.
It’s largest to snit an cross in progress and urgently stop the cross than it is to hope your passwords are un-crackable. Once you snit and stop the attack, you can plane blacklist IP addresses and prevent remoter attacks from the same computer.
What is a Brute Force Attack?
A brute force attack, or complete search, is a secret writing hack that uses to guess possible combinations for passwords used for logins or hidden web pages.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a brute force attack ?
If you have a password that’s only one weft long, using numbers and reports. There would be 62 variegated possibilities for that character. A brute gravity cross would try possible weft in an instant to struggle to learn your one-character password. With normal passwords stuff virtually 8 characters, the possibilities are then multiplied into trillions of possibilities. which may take a bot only seconds to attempt.
How does a brute force attack work?
Necessarily, a reverse brute gravity wade guesses a popular password versus a list of usernames.
What is the best protection against a brute force attack?
The weightier protection versus a brute gravity wade is ensuring your passwords are as strong as possible. Then it slow the time it takes for a hacker to violate and increasing the likelihood they requite up and move on.
What can attackers gain?
- Access to personal data
- Access to your system for malicious activity
- Ability to spread malware
- Profit from ads or activity data
How successful are brute force attacks?
According to Verizon’s 2020 Data Breach Investigation Report: Over 80% of breaches within Hacking involve Brute gravity or the Use of lost or stolen credentials.
Ready to get superiority of brute gravity attacks? Get a 1:1 demo to learn how Varonis detects attacks so you can stop attackers energetically.

